一、简介 如下图所示,按照界面编写的方式,可以分为传统布局和新型布局两种。 1.线性布局: 是平常练习demo时最常用的布局,分为水平、垂直方向两种线性布局,即设置其属性orientation:vertical或horizontal。【注:在不指定方向时,默认为horizontal,即
一、简介
如下图所示,按照界面编写的方式,可以分为传统布局和新型布局两种。
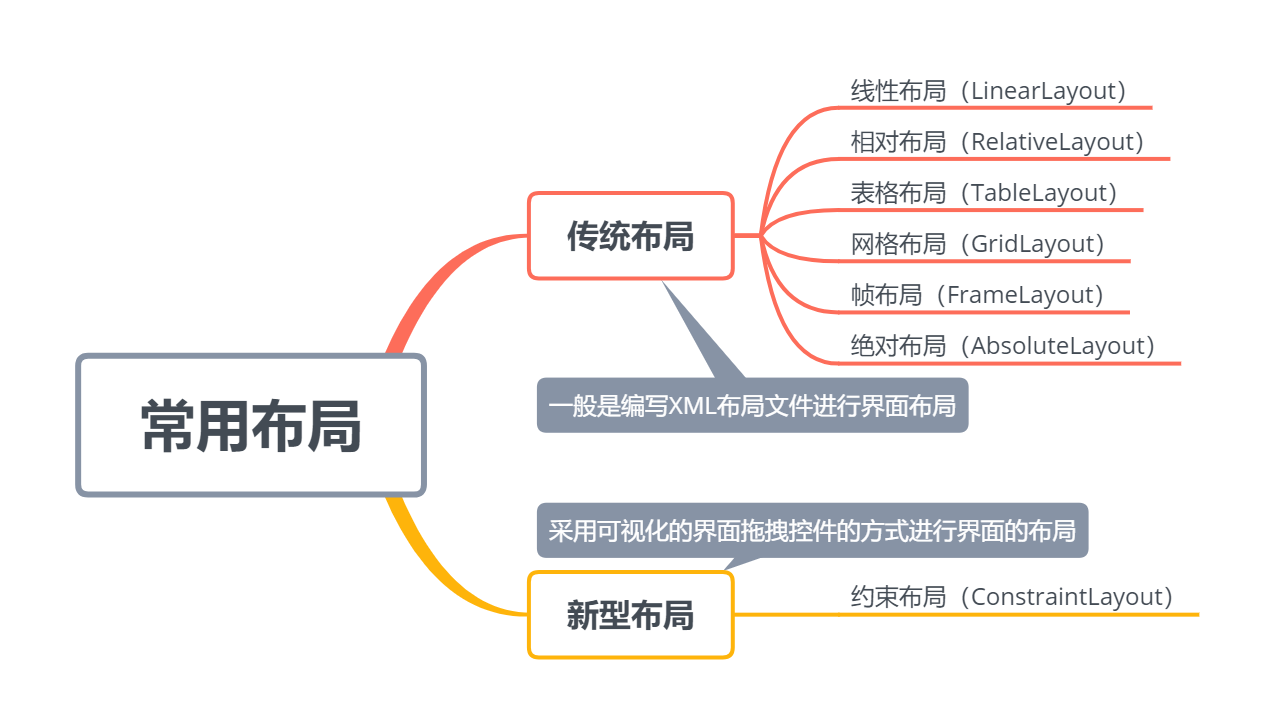
1.线性布局:是平常练习demo时最常用的布局,分为水平、垂直方向两种线性布局,即设置其属性orientation:”vertical或horizontal”。【注:在不指定方向时,默认为horizontal,即水平方向】
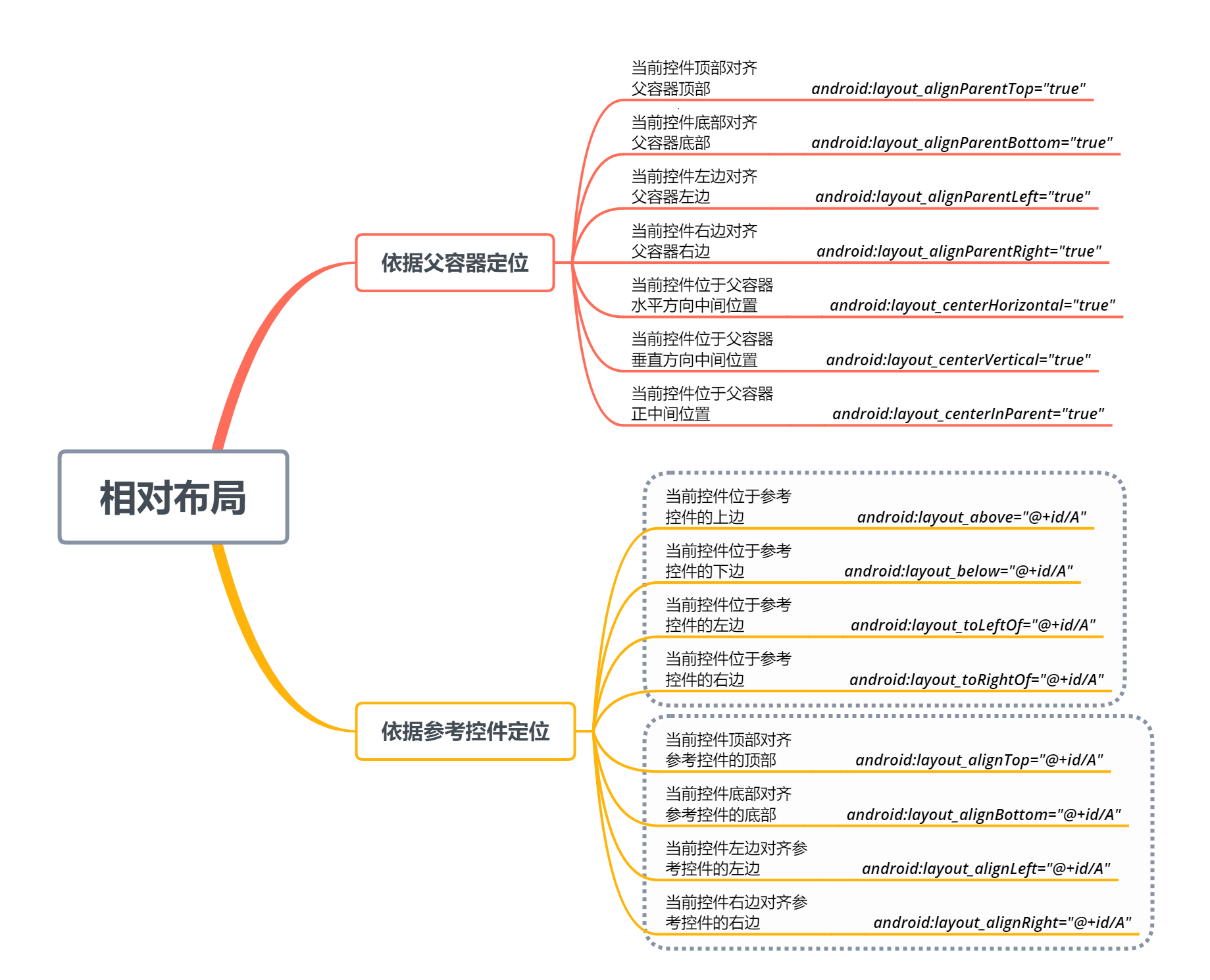
2.相对布局:依据某一控件的位置,来确定另一控件的位置,即另一控件相对于当前控件的位置。
3.表格布局:适用于多行多列的布局方式,通过表格方式来布局控件的位置,并且每个TableLayout由多个TableRow(表示行)组成。
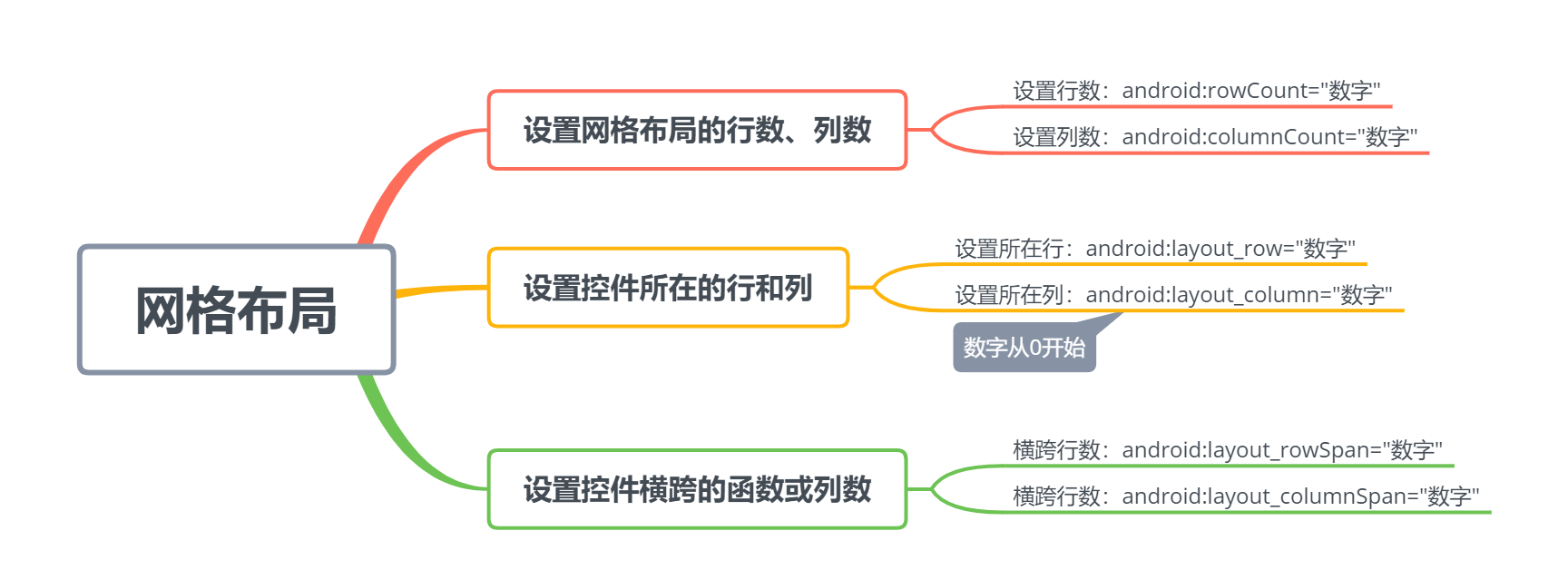
4.网格布局:是在Android4.0之后引入的一个新布局,和上面的TableLayout有点类似,但GridLayout比TableLayout更加好用、灵活。
5.帧布局:放入的所有控件都会被依次放在左上区域,因此下一个控件会重叠覆盖上一个控件,且无法为控件指定一个确切的位置。一般用于浏览单张图片。
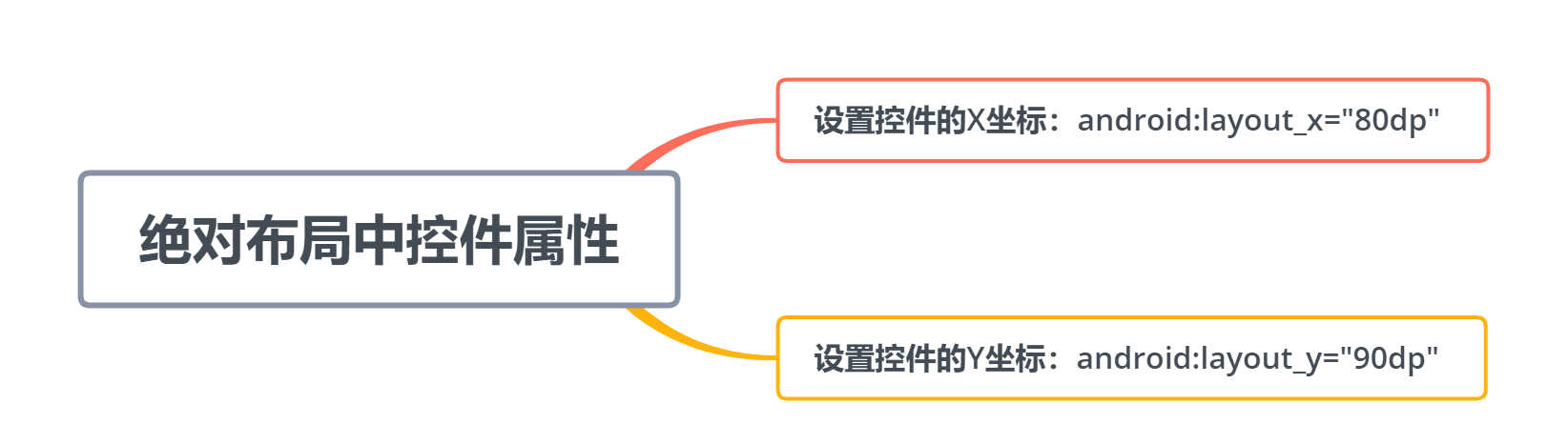
6.绝对布局:这个布局一般不会使用。屏幕的左上角为原点(0,0),横轴为x轴且向右为递增,纵轴为y轴且向下为递增,依据layout_x及layout_y属性分别设置控件的X及Y坐标。
7.约束布局:先说一下约束布局相对于传统布局的优势:①采用可视化的界面,拖拽控件即可完成界面的布局;②解决布局嵌套过多的问题,采用约束的方式来指定各个控件的位置和关系的,它有点类似于RelativeLayout,但远比RelativeLayout要更强大。
二、常用属性
2.1 所有布局的公有属性
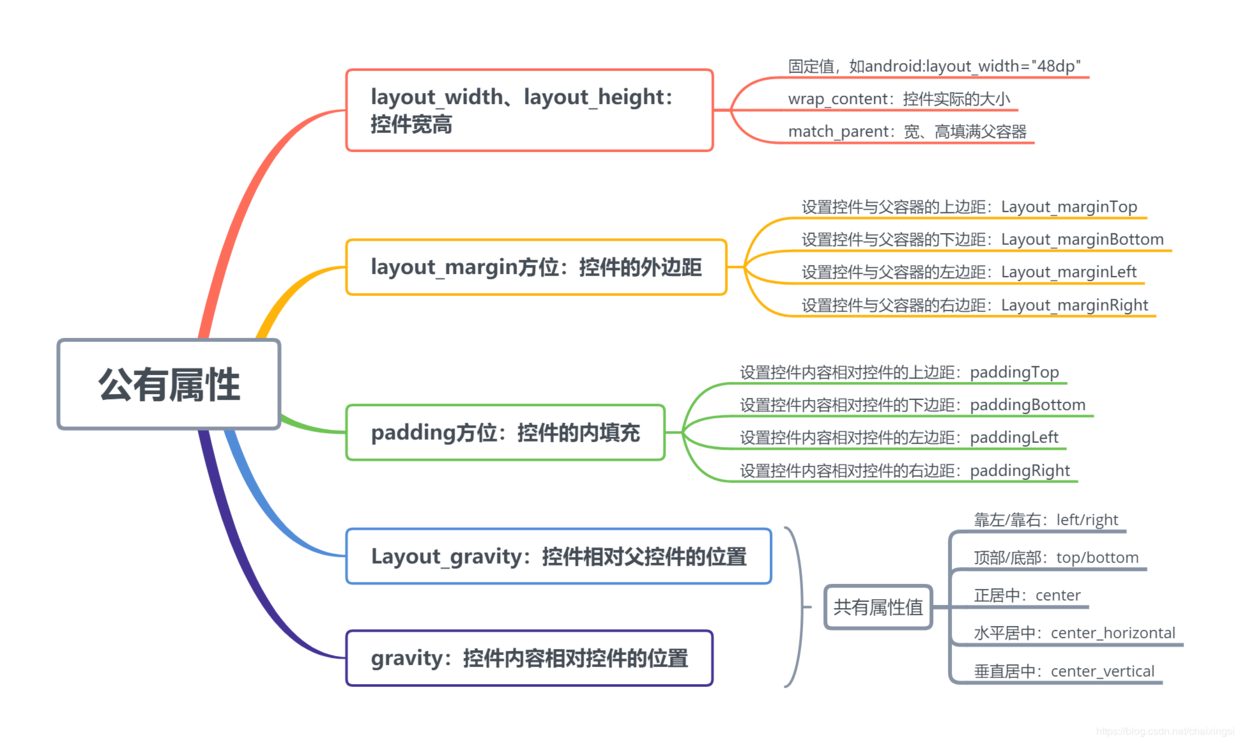
2.2 各个布局的特有属性
2.2.1 线性布局
- 在不指定线性布局方向的情况下,默认采用水平布局。
- 为了完全按比例分配剩余空间,我们一般将控件的 layout_width 或 layout_height 设置为 0dp,然后分别设置其权重值。【这里仅考虑常用的,至于宽设置为 wrap_content 或 match_parent 请自行尝试即可】
例:水平方向上有 3 个 TextView,设置权重为 1:1:1,则代码如下:
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"><!--不指定方向的情况下默认为水平方向-->
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#00FF7F"
android:text="text1" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#00BFFF"
android:text="text2" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#FA8072"
android:text="text3" />
</LinearLayout>运行结果如下: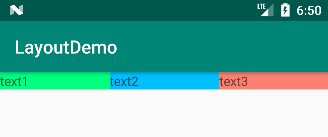
将权重比例改为 1:2:3,运行结果如下。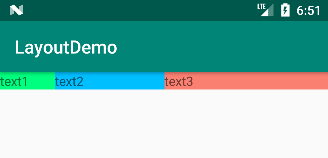
2.2.2 相对布局
2.2.3 表格布局
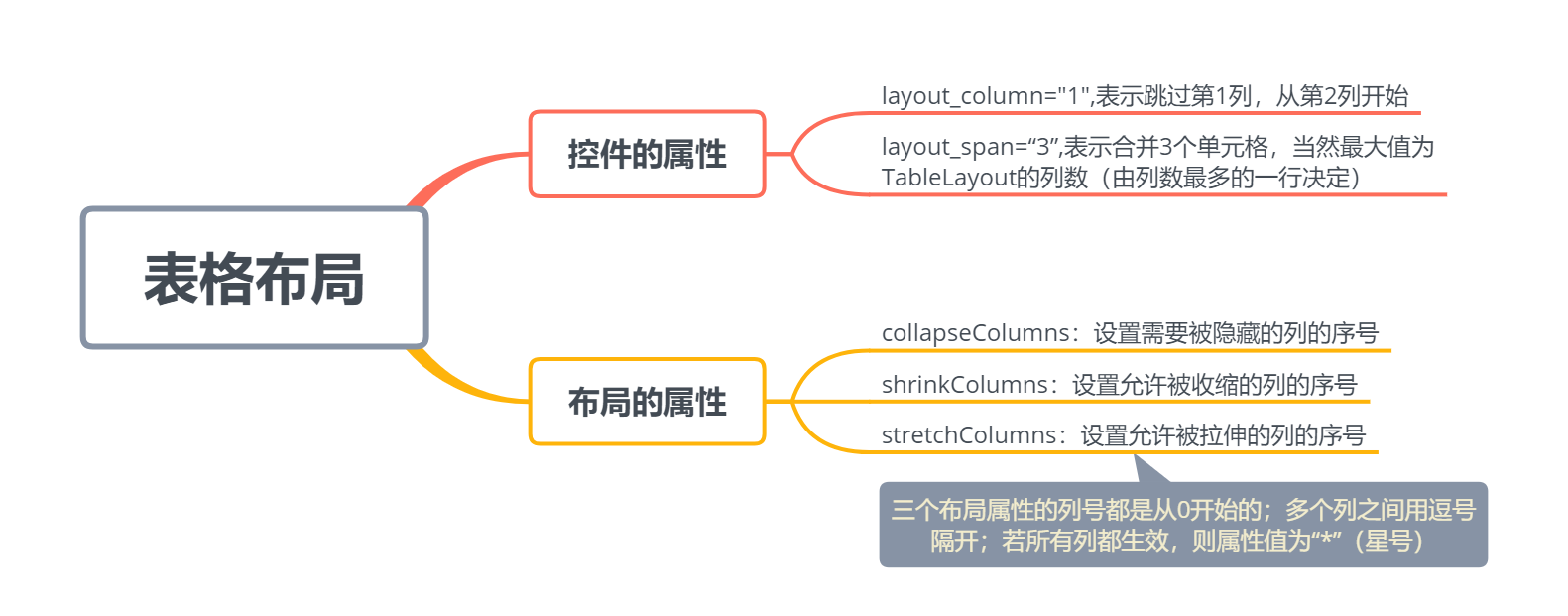
下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".TableLayoutActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#ff1493"
android:text="我独占一行" /><!--这里的文本框没有设置宽度,默认为父容器的宽度-->
<TableRow
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button android:text="button1" />
<Button android:text="btn2" />
<Button android:text="button3" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<!--设置layout_column属性,这里是跳过第1列,从第2列开始放置控件-->
<Button
android:layout_column="1"
android:text="button44444" /><!--该按钮文本最长,决定了该列的宽度-->
<Button android:text="b5" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button android:text="button6" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<!--设置layout_span属性,这里是合并3个单元格,即该按钮占3个单元格-->
<Button
android:layout_span="3"
android:text="button7" />
<Button android:text="button8" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>运行结果如下: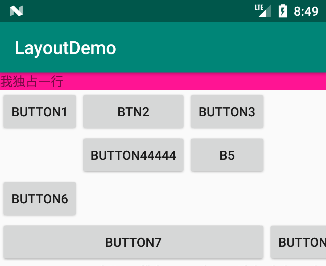
由上面的演示可以看出:
- 如果直接在 TableLayout 中添加控件,则该控件将占满一行,如第一行的文本框独占一行。
- 若要在一行上放置多个控件,则需要在控件的外层添加一个 TableRow 容器,如第 2、3、4、5 行放置了不同个数的的按钮。
- TableRow 容器中控件的个数决定了该行有多少列(如图分别有 1,3,2,1,2 列),而 TableLayout 的列数由控件最多的 TableRow 决定(整个布局有 3 列)。
- TableLayout 的列的宽度由该列中最宽的单元格决定,如 Button44444 按钮决定了第二列的宽度。
- 设置 layout_column 属性,这里是跳过第 1 列,从第 2 列开始放置控件。
- 设置 layout_span 属性,这里是合并 3 个单元格,即该按钮占 3 个单元格。
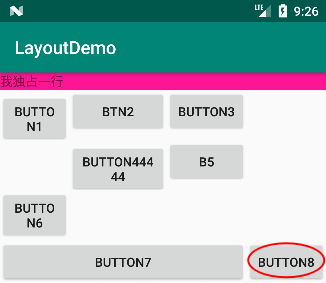
请依次添加添加以下布局属性: ① 收缩 1、2 列:
android:shrinkColumns="0,1"运行结果如下:显示不完全的 button8 显示完全了,并且 Button1、Button44444、Button6 按钮有收缩。
②隐藏第 1 列:
android:collapseColumns="0"运行结果如下:由于第 4 行仅有一个按钮,则整个第四行隐藏。
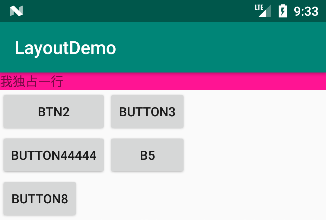
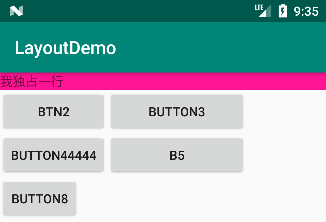
③ 伸展第 3 列:
android:stretchColumns="2"运行结果如下:由于仅有第 2、3 行有第三列,并且 Button3 与 B5 有拉伸。
2.2.4 网格布局 GridLayout 相关属性如下:
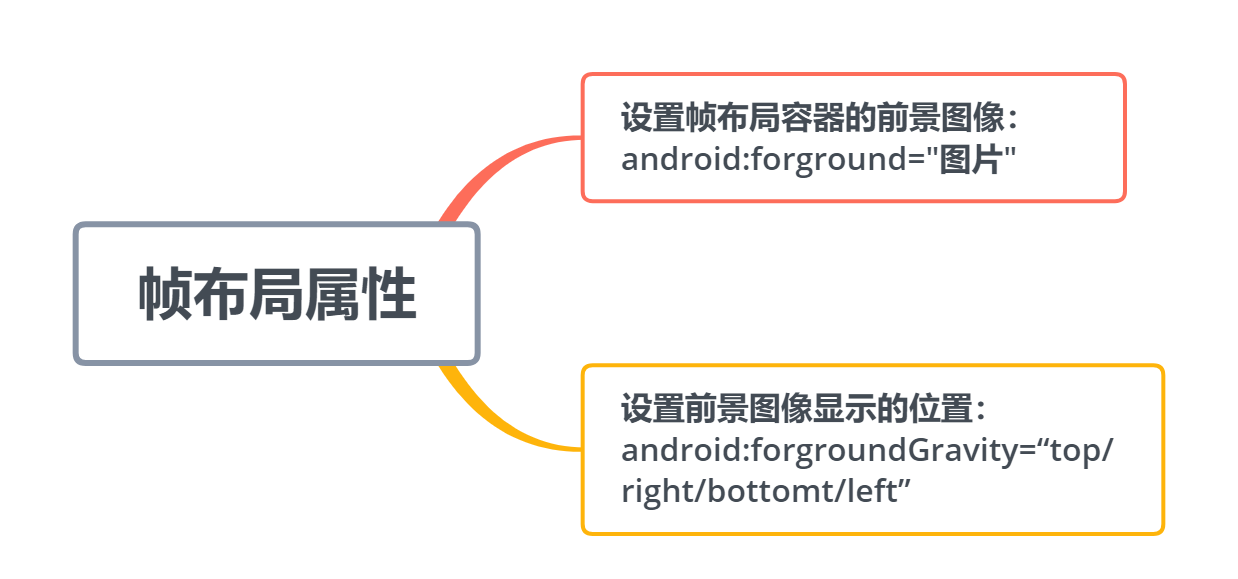
2.2.5 帧布局
- 帧布局是这几种布局中最简单的布局,添加到其中的控件默认会放到布局区域的左上角;
- 帧布局没有任何的定位方式,后一个控件会覆盖前一个控件;
- 帧布局的大小有控件中最大的控件决定;
注:设置前景图像的位置可以两个属性叠加,例如右下角:bottom|right。
2.2.6 绝对布局 绝对布局很少使用,一般有两个常用控件属性:
2.2.7 约束布局 约束布局是 Google 推荐的一种布局,有关于其拖拽控件、添加约束、借助 Inspector 设置属性、Gidelines 的使用以及自动添加约束的功能
最后
如果你看到了这里,觉得文章写得不错就给个赞呗!欢迎大家评论讨论!如果你觉得那里值得改进的,请给我留言。一定会认真查询,修正不足,定期免费分享技术干货。感兴趣的小伙伴可以点一下关注哦。谢谢!

 成为VIP
成为VIP